In today’s rapidly changing digital world, cybersecurity threats have become a major risk for organizations across every sector. Just this week, we’ve witnessed several significant cybersecurity incidents like LiteSpeed Cache Plugin vulnerabilities and Haliburton Attack.
Such as the exploitation of a serious vulnerability in the LiteSpeed Cache WordPress plugin and a cyber attack on the global oil services company, Haliburton. Hackers are continuously refining their strategies and taking advantage of new vulnerabilities.
Table of Contents
Introduction
In such a scenario, it’s crucial for businesses to remain vigilant and take proactive steps to safeguard their digital assets. In this post, we’ll discuss these latest cybersecurity challenges, analyze the wide-ranging impact of these incidents, and explore the evolving strategies of cybercriminals.
LiteSpeed Cache Plugin vulnerabilities
Hackers have begun exploiting a severe vulnerability in the LiteSpeed Cache WordPress plugin just a day after its technical details were disclosed. The vulnerability affects all versions up to 6.3.0 and allows attackers to escalate privileges without authentication.
This flaw originates from a weak hash check in the plugin’s user simulation feature, enabling attackers to brute force the hash value and create rogue admin accounts, leading to complete site takeovers.
Over 5 million sites use LiteSpeed Cache, but only 30% have updated to a safe version, leaving millions vulnerable. Wordfence has detected over 48,500 attacks exploiting this flaw in just 24 hours.
Users are urged to upgrade to version 6.4.1 or uninstall the plugin to protect their websites. This is the second major security issue with LiteSpeed Cache this year.
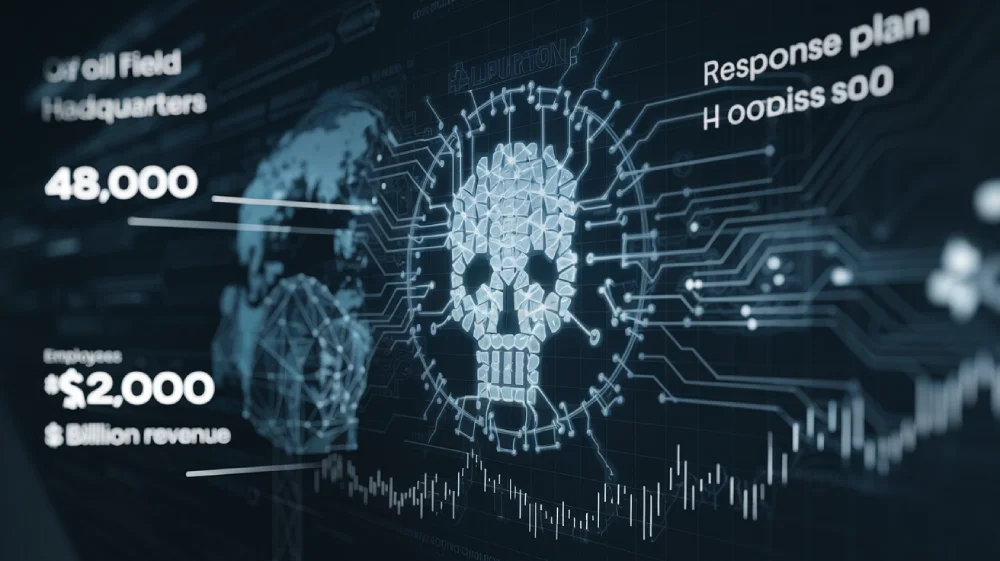
Haliburton Cyber Attack
Haliburton, one of the largest oil field services companies, confirmed that its networks were impacted by a cyber attack. The incident, which occurred recently, appears to have affected operations at the company’s Houston headquarters.

Though it’s unclear if other locations were impacted. Haliburton employs nearly 48,000 people globally and generated over $23 billion in revenue last year. The nature of the cyber attack remains unspecified, but some staff were reportedly told not to connect to internal networks.
Haliburton is working with external experts to address the issue and has activated its response plan. Despite the attack, the company’s stock remained stable.
Also Read
Liner AI: Price, Features, Ratings & Chatgpt vs Liner AI
Kling AI – How to Access Kling AI in India
The incident highlights ongoing cyber threats to the petroleum sector, though experts say disruptions to Haliburton’s operations are unlikely to affect gas supplies.
Velvet Ant and Cisco Switch Appliances
The threat group Velvet Ant, which earlier this year exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Cisco switch appliances. This allowed them to evade detection and maintain long-term access within networks.
The vulnerability enabled attackers with admin credentials to bypass the NX-OS command line interface and execute arbitrary commands on the underlying Linux OS, leading to the deployment of custom malware named Velvet Shell.
The malware operates invisibly, making detection by common security tools difficult. Velvet Ant’s shift to targeting network devices like Cisco switches demonstrates their evolving tactics in a multi-year espionage campaign.
This highlights significant security risks associated with third-party appliances, emphasizing the need for enhanced logging, continuous monitoring, and threat hunting to detect such advanced persistent threats.
Qilin Ransomware Group’s New Tactic
The Qilin ransomware group has adopted a new tactic, deploying a custom stealer to harvest credentials stored in Google Chrome.
This method, observed by Suos XOps during incident response, marks a concerning development in ransomware strategies.
The attack began with Qilin accessing a network via compromised VPN credentials, followed by an 18-day dormancy period likely used for reconnaissance. The attackers then moved laterally to a domain controller, modifying Group Policy Objects to execute a PowerShell script that collected Chrome-stored credentials across all logged-in machines.
These stolen credentials were exfiltrated, and traces were erased before deploying the ransomware payload. This approach complicates defense, as widespread credential theft can facilitate further attacks and make response efforts more challenging.
To mitigate risks, organizations should enforce strict policies against storing credentials in browsers, implement multi-factor authentication, and apply least privilege principles.
ARRL Ransomware Attack
The ARRL, the American Radio Relay League, a national association for amateur radio enthusiasts in the United States, reported that in early May, its network was compromised by threat actors using dark web-purchased information.
Also Read
Liner AI: Best Machine Learning Without Code AI Tool
Viggle AI : Viral Tauba Tauba Dance Meme Editing – Step-by-Step Guide
The attackers infiltrated both on-site and cloud-based systems, deploying ransomware across various devices, from desktops to servers. The highly coordinated attack took place on May 15th, leading to significant disruption.

Despite ARRL being a small nonprofit, the attackers demanded a multi-million dollar ransom. After some tense negotiations, ARRL paid a million-dollar ransom, largely covered by insurance. The organization quickly formed a crisis management team and involved the FBI, who categorized the attack as uniquely sophisticated.
Most systems have been restored, with the Logbook of the World back online within four days. ARRL is now simplifying its infrastructure and establishing an Information Technology Advisory Committee to guide future IT decisions.
SolarWinds Hotfix Release
SolarWinds has released a second hotfix for its Web Help Desk software to address critical vulnerabilities, including a serious issue with hardcoded credentials introduced in the first hotfix. This flaw, with a CVSS score of 9.1, could allow remote unauthenticated users to access and modify internal data.
The new hotfix removes the hardcoded credentials, fixes an SSO issue, and resolves the critical remote code execution vulnerability that the initial hotfix aimed to address.
CISA quickly added the RCE bug to its known exploited vulnerabilities catalog, indicating it may have been exploited in the wild. Organizations are urged to apply the latest hotfix immediately to secure their systems.
Lingo Telecom’s Fine Over AI-Generated Robo Calls
Lingo Telecom will pay a $1 million fine for transmitting deceptive robocalls in New Hampshire that used AI to spoof President Biden’s voice, violating federal caller ID rules.
The FCC announced that the robocalls, sent before the New Hampshire primary, were arranged by political consultant Steve Kramer, who is also facing a $6 million fine and criminal indictment. The FCC emphasized the need for transparency in AI usage in communications.
Also Read
WA Notifier – How to send bulk messages using WhatsApp API? Step By Step Guide
Character AI – Best AI character Chatbot – Rise And Fall of CharacterAI
Lingo Telecom also agreed to a compliance plan to prevent future violations.
Georgia Tech Lawsuit Over Pentagon Contract Cybersecurity Standards
The Justice Department is suing the Georgia Institute of Technology and an affiliated company for allegedly failing to meet required cybersecurity standards for Pentagon contracts.
The lawsuit, backed by the False Claims Act, reports that Georgia Tech’s Advanced Systems Technology (AST) Laboratory did not develop a proper system security plan as mandated by the Department of Defense and falsely reported their cybersecurity assessments to the Pentagon.

Despite implementing a plan in February 2020, the lab reportedly failed to cover all necessary devices. The whistleblower lawsuit, filed by two former Georgia Tech cybersecurity team members, alleges a lack of enforcement of cybersecurity regulations at the university.
Georgia Tech disputes the claims, stating that the lawsuit misrepresents their commitment to innovation and integrity and insists there was no breach or data leak involved.
Dustin Moody, a supervisory mathematician at NIST, shared insights into the development of post-quantum cryptography standards. He noted that around a decade ago, the team at NIST began scaling up their efforts in response to growing advancements in quantum computing.
Although quantum computers aren’t yet large enough to compromise current cryptographic systems, the potential threat they pose in the future necessitated the early establishment of new cryptographic standards.
Also Read
WA Notifier – How to send bulk messages using WhatsApp API? Step By Step Guide
Kling AI – How to Access Kling AI in India
To address this, NIST initiated an international competition in 2016 to identify the best algorithms for post-quantum cryptography. This process involved rigorous evaluation and analysis, both internally and by the global cryptographic community.
The competition resulted in the submission of 82 algorithms from teams around the world. Over several years, these algorithms were thoroughly tested, with the strongest ones surviving multiple rounds of scrutiny.
In July 2022, NIST announced the four algorithms that would be standardized as a result of this process. Since then, NIST has been working to finalize the standards for these algorithms, with three having been officially released in recent weeks.
Overview of the Post-Quantum Cryptography Standards
Moody explained that the NIST team was focused on two primary cryptographic functionalities: key establishment (or encryption) and digital signatures.
Digital Signatures:
- Crystals Dilithium: This algorithm is based on lattice structures and is expected to be the main digital signature algorithm used. It offers strong security and performance, making it suitable for most applications.
- Falcon: Also based on lattices, Falcon has smaller key sizes but requires complex floating-point arithmetic for implementation. While it is more efficient in certain applications, its complexity might limit its use in others.
- SPHINCS+: This algorithm is based on a different concept, providing an alternative to lattice-based algorithms. Although slower and larger, it offers a more conservative security analysis, making it a viable choice for those prioritizing security.
Key Establishment:
- Crystals Kyber: Like Dilithium, Kyber is based on lattice structures and emerged as the most promising algorithm for key establishment in the post-quantum era. Its combination of performance and security led to its selection as the primary algorithm in this category.
The three algorithms—Kyber, Dilithium, and SPHINCS+—have been published in final form as Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) after a period of public comment and minor revisions.
Also Read
WA Notifier – How to send bulk messages using WhatsApp API? Step By Step Guide
Kling AI – How to Access Kling AI in India
The fourth algorithm, Falcon, is still in the process of standardization. Due to its complex implementation, NIST is taking additional time to ensure the standard is thoroughly developed, with plans to release it by the end of 2024.
Cloudflare Introduces the Connectivity Cloud
The IT landscape has evolved dramatically, with employees, applications, and networks distributed across various environments. This shift has resulted in poor visibility, security gaps, and increased risk for organizations.
Also Read
WA Notifier – How to send bulk messages using WhatsApp API? Step By Step Guide
Kling AI – How to Access Kling AI in India
Addressing these challenges, Cloudflare has unveiled the first-ever Connectivity Cloud. This solution aims to secure and manage diverse IT environments effectively. For more details, visit Cloudflare’s website to learn how to protect your business comprehensively.
Phishing Simulation Mishap at UC Santa Cruz
In an attempt to enhance phishing awareness, UC Santa Cruz conducted a simulation that unfortunately caused unintended panic. On August 18th, the university sent out an email with the alarming subject line: “Emergency Notification: Ebola Virus Case on Campus.” Students and staff were understandably distressed, only to discover later that it was a simulated phishing exercise.
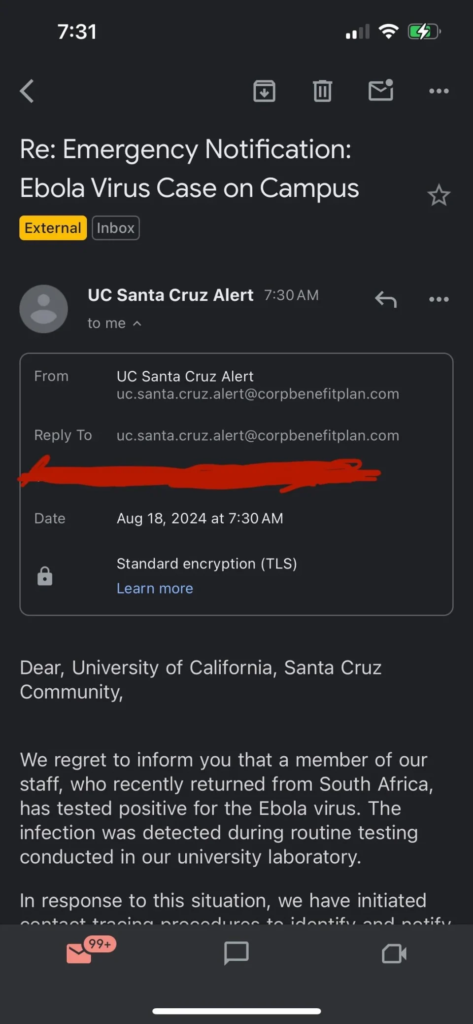
The email, designed to mimic a real phishing scam, urged recipients to log in for more details—a classic phishing tactic. However, the choice of an Ebola outbreak as the subject matter backfired, triggering widespread concern and prompting the Student Health Center to issue a clarification.
The university’s Chief Information Security Officer quickly apologized, admitting that the simulation crossed a line and caused undue stress.
Also Read
WA Notifier – How to send bulk messages using WhatsApp API? Step By Step Guide
Kling AI – How to Access Kling AI in India
This incident highlights the importance of careful planning in security training exercises. Future simulations at UC Santa Cruz will focus on less alarming scenarios to educate the community without causing unnecessary panic.
Conclusion
Staying informed and proactive is crucial in navigating today’s complex cybersecurity landscape. From understanding advancements in post-quantum encryption to learning from incidents like the phishing simulation at UC Santa Cruz, each insight equips us to build stronger, more resilient security practices. We appreciate your engagement and commitment to this Post.
If you found this post helpful, please like, comment, and share it with others. And if you’re new to the blog don’t forget to subscribe our Newsletter for more AI tool and tech news insights. Thank you for reading!
If you liked the information in this blog post, then subscribe to our blog below
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the latest vulnerability in the LiteSpeed Cache WordPress plugin?
Hackers are exploiting a severe vulnerability in the LiteSpeed Cache plugin, affecting versions up to 6.3.0, allowing them to escalate privileges without authentication.
How did the Haliburton cyber attack affect the company?
The cyber attack impacted Haliburton’s networks, particularly at its Houston headquarters, although the extent of the disruption to other locations remains unclear.
What is Velvet Ant, and how does it target Cisco switches?
Velvet Ant is a threat group that exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Cisco switch appliances, allowing them to evade detection and deploy custom malware for long-term access.
What was the result of the ARRL ransomware attack?
The ARRL suffered a ransomware attack, leading to a million-dollar ransom payment. The organization has since restored most systems and is working on improving its cybersecurity.
What are the key components of NIST’s post-quantum cryptography standards?
NIST has standardized three algorithms—Crystals Dilithium, Crystals Kyber, and SPHINCS+—to protect against future quantum computing threats, with a fourth, Falcon, still in development.
If you liked the information in this blog post, then subscribe to our blog and share this article in your AI community.



